Differential Scanning Calorimeter distribute|what is differential scanning calorimetry : maker Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. Both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the . See more Resultado da 2 de set. de 2022 · Abra sua conta, é online, rápido e 100% grátis. 1. Bitcoin (BTC) O Bitcoin é a criptomoeda mais famosa do mundo, por isso não podemos deixar de incluí-la na lista de melhores criptomoedas do mercado. Atualmente, ela continua sendo uma das principais moedas virtuais em .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBSadly, watching YouTube videos of Hotel 626 is the only way to experience the game now and although this isn't quite as terrifying as playing it yourself, it will unfortunately have to do. Although it is undeniably cheesy .

what is differential scanning calorimetry
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. Both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the . See moreThere are two main types of DSC: Heat-flux DSC which measures the difference in heat flux between the sample and a reference (which gives it the alternative name Multi-Cell DSC) and Power differential DSC . See moreAn alternative technique, which shares much in common with DSC, is differential thermal analysis (DTA). In this technique it is the heat flow to the . See moreDifferential scanning calorimetry can be used to measure a number of characteristic properties of a sample. Using this technique . See more
The technique is widely used across a range of applications, both as a routine quality test and as a research tool. The equipment is easy to calibrate, using low melting indium at 156.5985 °C for example, and is a rapid and reliable method of thermal . See moreThe basic principle underlying this technique is that when the sample undergoes a physical transformation such as See moreThe result of a DSC experiment is a curve of heat flux versus temperature or versus time. There are two different conventions: exothermic reactions in the sample shown with a positive or . See more
There are various experimental and environmental parameters to consider during DSC measurements. Exemplary potential issues are . See more Differential thermal analysis (DTA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) are similar methods in which the response of a sample and a reference to a change in temperature.DSC enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific heat capacity, and purity analysis are also . Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in .
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is an experimental technique for measuring the energy necessary to establish a nearly-zero temperature difference between a test substance S . The aim of this paper was to investigate pore-size distributions in the nano-diameter range of wood and their alteration due to thermal modification of wood using thermoporosimetry, and to find out what consequences can be derived regarding the biological durability. Thermoporosimetry is a technique that is based on the measurement using . We have developed an analytical method to quantitatively analyze differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) experimental data. This method provides accurate determination of thermal properties such as equilibrium melting temperature, latent heat, change of heat capacity which can be performed automatically without intervention of a DSC operator. DSC is one of .
In this updated and fully revised second edition, the authors provide the newcomer and the experienced practitioner with a balanced and comprehensive insight into all important methods and aspects of Differential Scanning . Instrumentation. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) shows the basic components of a heat-flux differential scanning calorimeter. The sample and the reference materials are sealed within small aluminum pans and placed on separate platforms within the sample chamber.
This research addresses the growing need for fast and cost-efficient methods for microplastic (MP) analysis. We present a thermo-analytical method that enables the identification and quantification of different polymer types in sediment and sand composite samples based on their phase transition behavior. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was performed, and .
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a technique used to study thermal transitions in polymers and other materials. It works by heating a sample and reference simultaneously while measuring the difference in energy required to keep them at the same temperature. . Changes in water distribution may be correlated with changes in texture .

on the measurement using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The method is based on the fact that frozen water contained within small pores is at elevated pressure and therefore has a depressed melting temperature as a function of the appropriate pore diameter. In addition, the fiber saturation points (FSP) were determined by DSC.
Different Measuring Types of DSC Analysis Instruments. There are different types of DSC instruments, for example: Heat-Flux DSC: This type of DSC measures the heat flow between a sample and a reference which are being subjected to a controlled temperature program (heating, cooling or Isothermal Tests at controlled and constant temperature are called isothermal. . We describe an analytical method based on differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) for characterizing the total amount of encapsulated water droplets and their stability in W/O/W multiple emulsions. . Figure 8 (left) gives a thermoanalytical curve of a W/O emulsion with a bimodal droplet size distribution. The DSC curve was measured at a .Materials and methods: The analysis of zinc chloride was performed using powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), particle size distribution, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis/differential thermogravimetric analysis (TGA/DTG), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis), and Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) analytical . Abstract A new technique for determining the pore size distributions (PSDs) from the melting and freezing curves of water confined in pores, thermal porosimetry termed thermoporosimetry, has been established by combining some physical properties determined by a preceding study with iterative optimization of the layer of nonfreezable water. By applying the .
DOI: 10.1016/J.FOODRES.2008.05.009 Corpus ID: 96872711; Characterization of melting properties in dark chocolates from varying particle size distribution and composition using differential scanning calorimetry
dsc 600 differential scanning calorimeter
Melting properties in dark chocolates processed from varying particle size distribution (PSD), fat and lecithin content were studied using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Compositional parameters were PSD (D 90 (90% finer than this size) of 18, 25, 35 and 50 μm), fat (25%, 30% and 35%) and lecithin (0.3% and 0.5%) contents. Variations . Discover the science behind differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) - a crucial thermal analysis technique. This video provides a comprehensive overview of D.
Thin film based differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) was developed and utilized for the study of phase-transition kinetics in protein samples. . The analysis of the temperature distribution and heat conduction between the sample and reference cells suggests a minimal distance for negligible heat conduction between the sample and reference .DSC- Differential Scanning Calorimetry Instrument. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), is an undemanding and effective technique, utilized for examining the thermodynamic properties of thermally induced transitions. The . Using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), the acid site strength distribution in Na- and H-mordenites is investigated. Triethylamine (TEA) and ammonia are presorbed into the mordenites and then desorbed via a DSC programmed temperature increase from 50 to 600 °C. Various presorbing contact periods are used to throw light on the rate of . The fundamentals of the widest-spread methods of thermal analysis including a short excursion into differential scanning calorimetry are presented. Five practical examples illustrate the experimental approach for the measurement design .
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a method widely used to examine the melting or crystallization profile of cocoa butter and chocolate. The (perceived) ease of use makes the method very appealing not only in academia, but also in the chocolate industry. Our study presents a critical evaluation of the parameters that influence the generated information .Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) works by measuring the amount of energy absorbed or released by a sample (the heat flow) as it is subjected to a controlled heating or cooling cycle, or held isothermally at the same temperature. . DSC results can be influenced by the sample's morphology, surface area, or particle size distribution . 差示扫描量热仪(Differential Scanning Calorimetry,简称DSC)。 基本原理:DSC监测样品和参比温度差(热流)随时间或温度变化而变化的过程。 样品和参比处于温度相同的均温区,当样品没有热变化的时候,样品端和参比端的温度均按照预先设定的温度变化,温 .
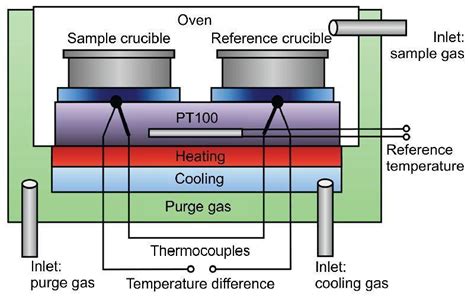
A Differential Scanning Calorimetry, or DSC, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (Cp) is changed by temperature. A sample of known mass is heated or cooled and the changes in its heat capacity are tracked as changes in the heat flow. This allows the detection of transitions like 2 Nanostructured coatings: sample preparation and system calibration 2.1 Sample preparation. An important aspect specific for thermal characterization of nanostructured coatings by thermal analysis using DSC is related to the very small mass ratio between coated materials and the substrate: any thermal effect associated to the system will be hindered by the .The heat-flux cell of DSC 214 Polyma measuring cell protective gas purge gas furnace block with heating heat flux sensor reference sample Working with DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimetry) involves not only the handling of a device, but also sample preparation, evaluation and interpretation of the resulting curves.The DSC 214 Polyma is a key .
In order to be recycled, polymers with different molecular masses, designed to be initially processed by different technologies such as thermoforming, injection or blow molding, are collected together. The melt viscosity of this material mixture will depend on the ratio of polymers having different molecular characteristics. The possibility of re-processing implies the use of .
Find here Differential Scanning Calorimeter, DSC Calorimeter manufacturers, suppliers & exporters in India. Get contact details & address of companies manufacturing and supplying Differential Scanning Calorimeter, DSC Calorimeter, Differential Scanning Calorimetry Instrumentation across India. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely programmed temperature change. DSC is very similar to DTA and gives much the same sort of information but DSC is more often used for quantitative measurement .
scratch test levels
Poker - Estoril Sol Casinos Portugal - ESC Online
Differential Scanning Calorimeter distribute|what is differential scanning calorimetry